
Loading...
29th June 2021

We have written a great deal over the last few years on the wealth polarising effect of monetisation. Given the significant increase in the Federal Reserve’s balance sheet through the COVID19 lockdowns, therefore, it should come as no surprise that the portion of net worth owned by America’s wealthy has increased again – nearly a third of all net worth in the US is in the hands of the Top 1% (see figure 1).
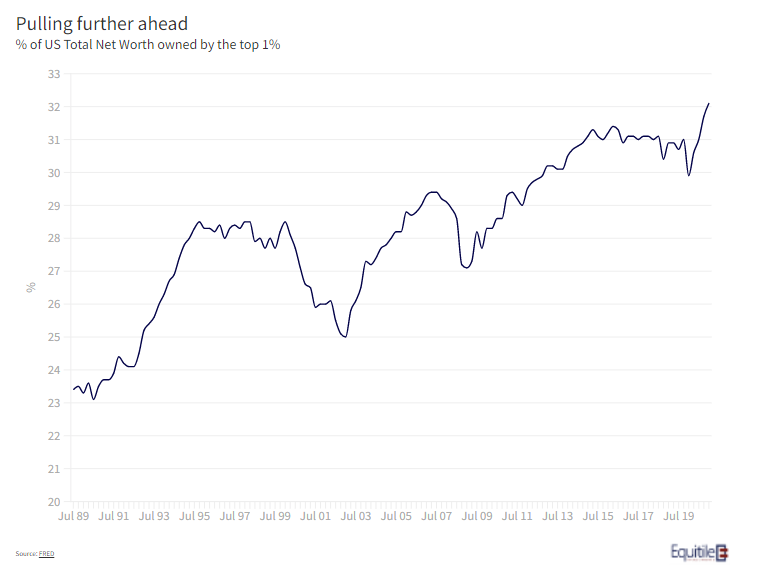
The most often cited cause of this is the Fed’s impact (although they largely deny this) on the price of assets held mainly by the well-off. There are, however, more subtle drivers too. The swings seen in asset markets, due to both COVID in 2020, and the longer-term effect rising leverage has on market volatility, has made it more difficult for the less-well off to hold on. In a bear market, as John Pierpont Morgan somewhat cynically pointed out, “stocks return to their rightful owners” and so if bear markets come more often and more sharply, then the rate of repatriation will only accelerate.
This might explain why, as shown in figure 2, the ownership of corporate equities and mutual funds in the US has become even more concentrated than for other forms of wealth. More than a half of all business equity, held either directly or indirectly, is held by the top one per cent of all owners. A trend that looks set to accelerate.
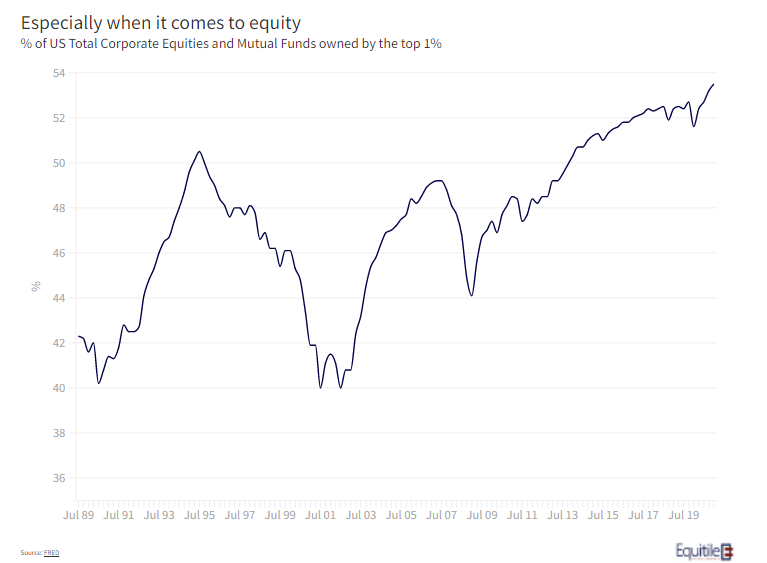
It may not only come down to the capacity to sustain losses, however. As in all western countries, good advice comes at a price. At Equitile we are not financial advisers but we talk to many advisers through the course of our business. As we see it, the crucial value of a good adviser is support and encouragement when the market has a set-back. A good adviser is in the best position to help investors overcome their natural behavioural aversion to loss, and to help plan their broader finances to make this easier. With good personal advice now scarce and expensive for those of lesser means, the ability to sustain losses floats ever upwards.
One intriguing move by the top 1% is their move away from bonds. Their holdings of debt assets (figure 3) has fallen from more than 60% to 40% of all debt assets in the last two decade - they sold aggressively throughout the COVID crisis.
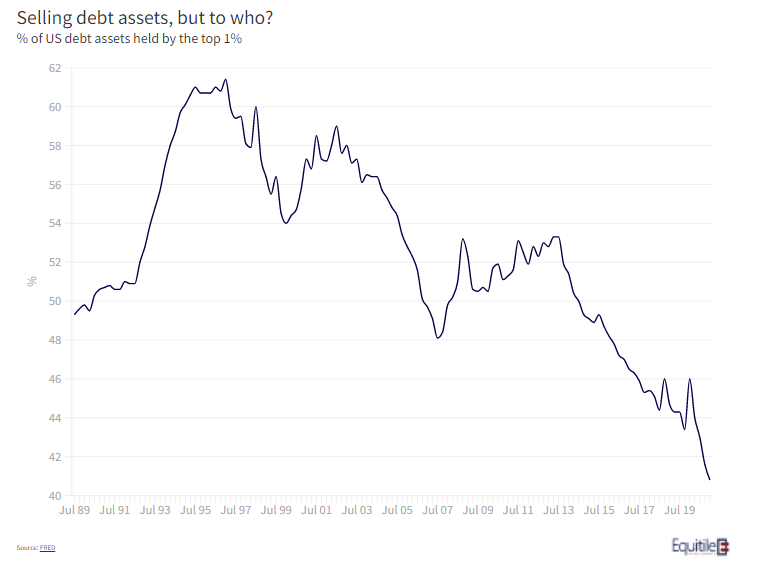
With real interest rates in the US the most negative since the 1970’s, the potential for capital destruction through financial repression, for bond holders at least, is rising sharply. Perhaps the top 1% know this instinctively, or perhaps they are just better advised.